HPV 31 identification

Improve cervical cancer screening with identification of HPV 31
Only an HPV assay with extended genotyping can individually identify hr-HPV genotypes beyond HPV 16 and 18, including HPV 31, which poses a similar risk for cervical precancer as compared to HPV 18 and should be managed similarly.1-4
HPV 31 is the second highest-risk HPV genotype for CIN3+ disease1,2,5
Bayesian model for risk of ≥CIN3 by HPV genotype
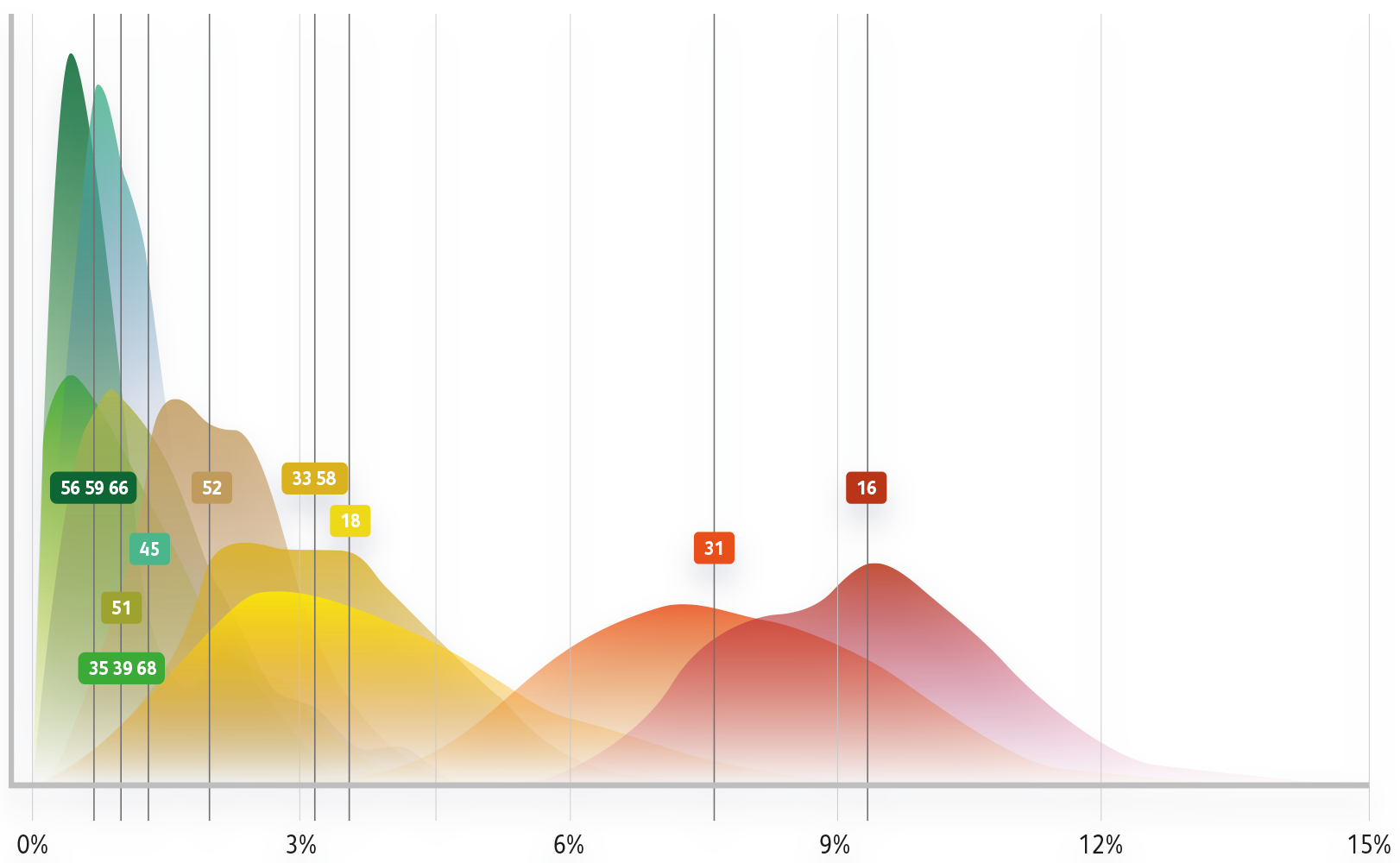
Stoler MH et al. Gynecol Oncol 2019;153(1):26–33.
In a US study from 2019, women 25 years and older with HPV 31 and normal cytology had an immediate risk for CIN2+ of 12.1%, similar to HPV 16, with a risk of 11.6%.1
Risk of CIN2+ by HPV type in women > 25 years with normal cytology1
Created from information provided in Stoler MH et al. Gynecol Oncol 2019;153(1):26–33.
In a US study from 2019, women 25 years and older with HPV 31 and normal cytology had an immediate risk for CIN3+ of 7.5%, similar to HPV 16, with a risk of 8.1%.1
Risk of CIN3+ by HPV type in women > 25 years with normal cytology
Created from information provided in Stoler MH et al. Gynecol Oncol 2019;153(1):26–33.
ASCCP, American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology; CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; FDA, Food and Drug Administration; HC2, Hybrid Capture 2; HPV, human papillomavirus; hr, high risk
1. Stoler MH et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2019;151(4):433–42.
2. Bonde JH et al. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24(1):1–13.
3. Monsonego J et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2015;137(1):47-54.
4. Perkins RB et al. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24:102–31.
5. Bonde J et al. Int J Cancer. 2019;145:1033–41.
6. Schiffman M et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2015;138(3):573–8.
7. Schiffman M et al. Int J Cancer. 2016:139:2606–15.
8. Schiffman M et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(1):52–9.
What are CIN 1, CIN 2 and CIN 3?
CIN is graded by how deep the cell changes go into the surface of the cervix. It is graded into: CIN 1, CIN 2 & CIN 3.1
CIN 1

Surface layer of the cervix cells
CIN 1 means one third of the thickness of the surface layer is affected.
Cells showing CIN 1 will often return to normal without any treatment. Recommendations are to prescribe further cervical screening tests or colposcopies to check whether your patients’ cells have improved. If these tests show the CIN 1 is not improving, you may recommend treatment.
CIN 1 is also called low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL)2
CIN 2

Surface layer of the cervix cells
CIN 2 means two thirds of the thickness of the surface layer is affected.
CIN 2 has a risk of developing into cervical cancer.
CIN 2/3 is also called high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) and it is a precancerous condition2
CIN 3

Surface layer of the cervix cells
CIN 3 means the full thickness of the surface layer is affected.
CIN 3 is also known as carcinoma-in-situ.
CIN 3 has a higher risk of developing into cervical cancer.
CIN 2/3 is also called high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) and it is a precancerous condition2




























